TURKEY: GANODERMA LUCIDUM POLYSACCHARIDES ACCELERATE RECOVERY FROM TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURY
In the past, it was heard that some people suffered traumatic brain injury due to accidents. In addition to receiving regular treatment, they also took a lot of Ganoderma lucidum. As a result, the speed and effect of recovery were beyond expectations. The 63rd issue (Spring 2014) of "Healthy Ganoderma" issued by the Microbiology Culture and Education Foundation also introduced six real cases of using Ganoderma lucidum to reverse the trauma caused by car accidents.
Is Ganoderma lucidum so "magical"? A report published in "Korean Journal of Neurotrauma" (South Korean Journal of Neurotrauma) by Dicle University in Turkey in October 2017 confirmed through animal experiments that the polysaccharide extract of Ganoderma lucidum fruiting bodies can indeed accelerate the recovery of brain trauma, and its mechanism of action is related to reducing oxidative stress and slowing down inflammation.
The researchers used the artificial method of "falling from height" to cause brain injuries in rats. Half of them (16 rats) did not receive any treatment (brain trauma group). The other half (brain trauma + Ganoderma lucidum group) was fed with Ganoderma lucidum at a given daily dose of 20 mL per kilogram of body weight 30 minutes after the trauma (each mL of Ganoderma lucidum water extract contains 2 mg of polysaccharides). The brain trauma of the rats is evaluated after seven days. The experiment also has used normal rats (control group) and normal rats fed with Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharide (Ganoderma lucidum group) to compare with the previous two groups.
Bleeding in the brain can cause inflammation, increase the oxidative pressure in the brain (antioxidant enzymes will decrease, and the number of free radicals will increase), and may also cause edema (which squeezes the brain tissue and damages it). The original blood-brain barrier (the natural barrier between blood vessels and the brain that can block foreign substances from entering the brain) will also be destroyed, causing more white blood cells to infiltrate the brain or causing brain infections, making the inflammation more serious.
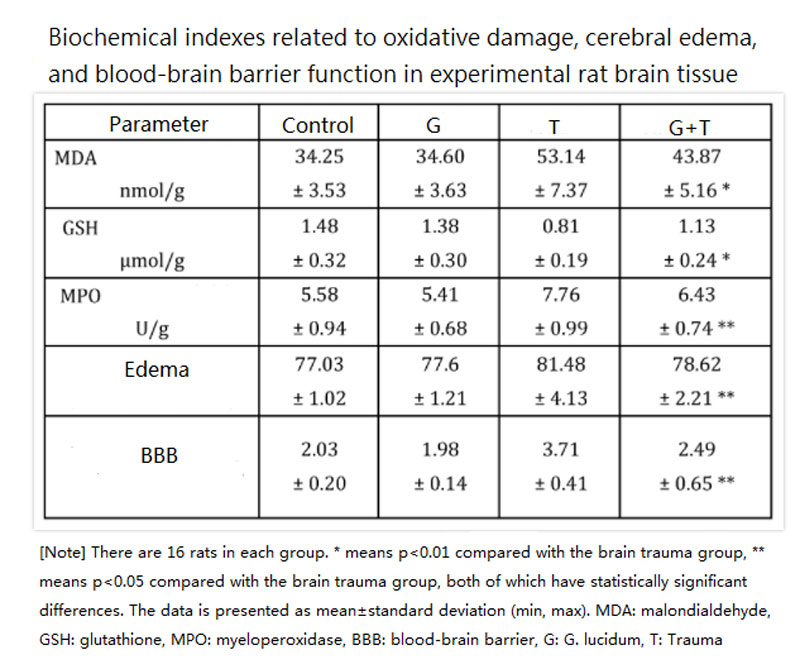
These conditions are not conducive to the recovery of brain tissue from trauma. But according to the results of animal experiments in this report, after brain-traumatized rats were treated with Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharide for seven days, their brain tissue is less damaged by free radicals (MDA reduces), the antioxidant enzyme GSH that neutralizes free radicals in the brain increases, white blood cell inflammation is less severe (the secretion of peroxidase MPO is less), cerebral edema is also significantly improved, and the permeability of the blood-brain barrier is also closer to normal— all values are significantly different from those of brain-traumatized rats that have not received any treatment (see the table below).
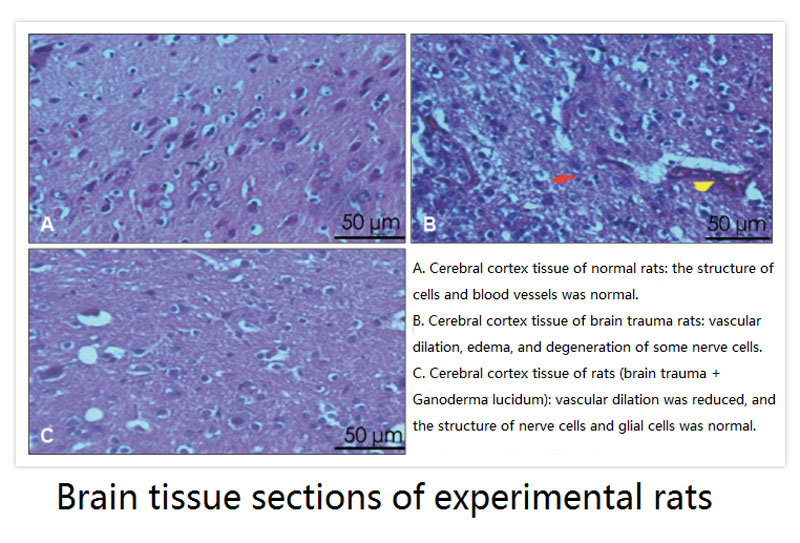
In addition, it can be seen from the tissue sections of the cerebral cortex that Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharides can improve blood vessel dilation and edema, repair nerve cells, and accelerate the recovery of the injured brain (as shown below). The cerebral cortex refers to a connected skin-like structure with many wrinkles wrapped in the outer layer of the brain. It is responsible for higher-level feelings and thinking abilities. Therefore, the recovery of this area is of great significance.
The researchers also tested three other important indicators in rat brain tissue, including protein kinase p38 MAPK, which is positively related to inflammation, vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), which is necessary to repair vascular structure, and microglial cell, which is responsible for removing damaged nerve cells and pathogens.
It was found that, compared with brain-traumatized rats that did not eat Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharides, although the activity of p38 MAPK was still detected in the brain-traumatized rats that ate Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharides, (indicating that the reaction was ongoing but it had been controlled and would not worsen), their vascular endothelial growth factors and microglial cells increased significantly, indicating that Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharide is beneficial to the repair and reconstruction of cerebral vessels and cranial nerves.
The above experimental results show the effect of continuous administration of Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharides for seven days after the brain is injured. Researchers believe that if the appropriate dose of Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharides can be used as adjuvant therapy after brain trauma occurs, it will be very helpful for alleviating inflammation and cerebral edema, or for protecting nerve cells and glial cells.
[Source] Özevren H, et al. Ganoderma Lucidum protects rat brain tissue against trauma-induced oxidative stress. Korean J Neurotrauma. 2017; 13(2): 76-84.
END
About the author/ Ms. Wu Tingyao
Wu Tingyao has been reporting on first-hand Ganoderma lucidum information since 1999. She is the author of Healing with Ganoderma (published in The People's Medical Publishing House in April 2017).
★ This article is published under the exclusive authorization of the author
★ The above works cannot be reproduced, excerpted or used in other ways without the authorization of the author
★ Violation of the above statement, the author will pursue its related legal responsibilities
★ The original text of this article was written in Chinese by Wu Tingyao and translated into English by Alfred Liu. If there is any discrepancy between the translation (English) and the original (Chinese), the original Chinese shall prevail. If readers have any questions, please contact the original author, Ms. Wu Tingyao.